Most cars these days use what is called a four-stroke combustion cycle to convert gasoline into kinetic motion. This four-stroke approach is known as the the Otto cycle, in honor of Nikolaus Otto who invented it in 1867.
-
Intake stroke- air and fuel are taken into the cylinder as the piston moves downwards.

-
Compression stroke- where the air and fuel are compressed by the upstroke of the cylinder.

-
Combustion stroke- compressed mixture is ignited and the expansion forces the cylinder downwards.
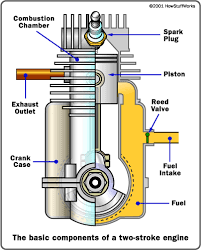
 two stroke four stroke
two stroke four stroke
-
Exhaust stroke- waste gases are forced out of the cylinder.

The intake and outlet ports open and close to allow air to be drawn into the cylinder and exhaust gases to be expelled.
So we understand that the engine is effectively a device which sucks in air, compresses it, ignites it and then blows the air out again to create power to the road wheels. In terms of the performance gains possible, there are a vast multitude of different techniques and technologies.
Intake stroke- air and fuel are taken into the cylinder as the piston moves downwards.
Compression stroke- where the air and fuel are compressed by the upstroke of the cylinder.
Combustion stroke- compressed mixture is ignited and the expansion forces the cylinder downwards.
two stroke four stroke
Exhaust stroke- waste gases are forced out of the cylinder.
First of all lets get a understanding of the different types of engine layouts commonly found in cars today. As Engines can come in an array of different designs, including Straight/Inline, V type, Boxer, Rotary Wankel and even Diesel:
straight engine :
V type :
boxer :
Rotary wankel :
Diesel :
